REGDOC-1.5.1, Application Guide: Certification of Radiation Devices or Class II Prescribed Equipment
Preface
This regulatory document is part of the CNSC’s Certification of prescribed equipment series of regulatory documents, which also covers servicing Class II prescribed equipment. The full list of regulatory document series is included at the end of this document and can also be found on the CNSC’s website.
This guide is intended to help applicants to prepare and submit applications to the CNSC for certification of radiation devices and Class II prescribed equipment. It assists applicants and licensees in complying with the Nuclear Safety and Control Act and regulations and ensures that:
- the radiation device or Class II prescribed equipment is safe to use
- adequate measures are in place to protect the environment, the health and safety of persons, and national security
- the design meets Canada’s international obligations
An electronic version of the application form is available at nuclearsafety.gc.ca. CNSC staff can provide additional guidance upon request; contact the CNSC at transport@cnsc-ccsn.gc.ca.
This document supersedes RD/GD-254, Application Guide Certification of Radiation Devices or Class II Prescribed Equipment, published in December 2010.
Guidance contained in this document exists to inform the applicant, to elaborate further on requirements or to provide direction to licensees and applicants on how to meet requirements. It also provides more information about how CNSC staff evaluate specific problems or data during their review of licence applications. Licensees are expected to review and consider guidance; should they choose not to follow it, they should explain how their chosen alternate approach meets regulatory requirements.
Nothing contained in this guide is to be construed as relieving any applicant or licensee from requirements associated with conventional codes and standards. It is the applicant or licensee’s responsibility to identify and comply with all applicable regulations and licence conditions.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
1.1 Purpose
This document provides guidance for the completion and submission of the application form for certification of radiation devices or Class II prescribed equipment, in accordance with the Nuclear Safety and Control Act (NSCA) and the regulations made under it.
1.2 Scope
This information is intended to help applicants prepare and submit applications to the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC) for the certification of radiation devices or Class II prescribed equipment. It provides a description of the type of information that should be included in an application for certification.
Class II prescribed equipment and radiation devices will hereafter collectively be referred to as prescribed equipment, as defined in section 20 of the General Nuclear Safety and Control Regulations.
1.3 Relevant legislation
The provisions of the NSCA and the regulations made under it that are relevant to this guide are as follows:
- Nuclear Safety and Control Act, paragraphs 37(2)(a) and (b) and 44(1)(b) and (c)
- Class II Nuclear Facilities and Prescribed Equipment Regulations, section 11
- Nuclear Substances and Radiation Devices Regulations, section 12
- Radiation Protection Regulations, section 20
- Packaging and Transport of Nuclear Substances Regulations, 2015
- General Nuclear Safety and Control Regulations, sections 15 and 20
- Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission Cost Recovery Fees Regulations;
Other legislation relevant to this guide is as follows:
- Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations
- Access to Information Act, sections 7, 8, 19 and 20
- Privacy Act, sections 18 to 24
- SSR-6, Regulations for the Safe Transport of Radioactive Material, 2018 Edition (PDF, 190 pages, 1.7 MB) published by the International Atomic Energy Agency
2. Certification Process
2.1 General
Paragraph 21(1)(h) of the NSCA empowers the CNSC to certify and decertify prescribed equipment. The Class II Nuclear Facilities and Prescribed Equipment Regulations and the Nuclear Substances and Radiation Devices Regulations stipulate application requirements for the certification of prescribed equipment. For the purpose of this document, prescribed equipment is limited to Radiation Devices under the Nuclear Substances and Radiation Devices Regulations and Class II prescribed equipment under the Class II Nuclear Facilities and Prescribed Equipment Regulations.
Prescribed equipment (which includes radiation devices and Class II prescribed equipment according to the General Nuclear Safety and Control Regulations) must be certified by the CNSC before it can be used in Canada. This certification is not to be construed as a licence for use, servicing, or installation.
An application for certification needs to be submitted to the CNSC in order for a certificate to be issued. Applicants for certificates should complete the application form for certification of radiation devices or Class II prescribed equipment (see appendix A). Upon receipt, the CNSC reviews the submission to determine if:
- the prescribed equipment is safe to use
- adequate measures are in place to protect the environment, the health and safety and security of persons, and national security
- the design meets Canada’s international obligations
If satisfied that the design meets the above requirements, the CNSC or a designated officer may issue a certificate for the prescribed equipment. The certificate will incorporate a description of the prescribed equipment. The required fee is applied as described in the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission Cost Recovery Fees Regulations.
Once a certificate has been issued, it applies only to the specific model designs listed and to the operating conditions associated with these models. Any significant changes (see glossary for definition) to the design or use of certified prescribed equipment, including upgrades or retrofits, must be submitted to the CNSC for approval prior to implementation.
2.2 Submitting an application
Typically, it is prescribed equipment manufacturers who submit applications for certification since they have ownership of the required application information (drawings, specifications, procedures, etc.) and seek to market the prescribed equipment. However, anyone may submit an application for certification of prescribed equipment, provided they are able to supply the necessary information to the CNSC.
Before submitting an application to the CNSC, ensure the following:
- the application is complete and signed by the appropriate authorities
- all supporting documents are attached, clearly identified and cross-referenced
- the designated payment is enclosed, if subject to the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission Cost Recovery Fees Regulations
For applicants wanting to submit the application physically, print a copy of the completed form, sign and date it, and mail it to the CNSC’s Directorate of Nuclear Substance Regulation at the address indicated below:
Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission
Directorate of Nuclear Substance Regulation
P.O. Box 1046, Station B
280 Slater Street
Ottawa, ON K1P 5S9
For applicants wanting to submit the application electronically, the completed form and supporting documentation can be submitted to the CNSC email address found at the bottom of the application form.
The applicant should keep a complete copy of the application for his records. All information submitted is subject to the provisions of the Access to Information Act (ATIA) and the Privacy Act.
2.3 Types of applications
The CNSC is authorized to certify and decertify prescribed equipment. Within this authority, the following types of applications for certification are processed:
New design certificate
For a new design, the applicant must complete all pertinent sections of the application form and submit it to the CNSC for approval.
For cost recovery fees, according to the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission Cost Recovery Fees Regulations, a new design application is considered as the assessment of a new prescribed equipment model.
Amendments to information on an existing certificate
Amendments are only required for significant changes (see glossary for definition) to the prescribed equipment. Where information has not changed from the existing certification, a simple reference to the information previously submitted should clearly identify the specific document(s) involved. If the amendment request is being made by an organization other than the manufacturer, justification should be provided on how the standards and designs are being maintained.
Once the CNSC is satisfied that an amendment is acceptable, it issues a new certificate for the modified design of the prescribed equipment, generally with the same expiry date as the existing certificate. The previously issued certificate remains valid until its expiry date, unless the CNSC formally informs the manufacturer and users that the certificate will be decertified. To facilitate tracking, the identification number of the new certificate will be identical to the one for the previously issued certificate except for the revision level.
For cost recovery fees, according to the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission Cost Recovery Fees Regulations, an amendment application is considered as the assessment of prescribed equipment similar to a certified prescribed equipment model.
Renewal of an existing certificate
Renewal applications are submitted for the continued use of an existing certified design prior to the expiry of the current certificate. Similar to an amendment application, where information has not changed from the existing certification, a simple reference to the information previously submitted should clearly identify the specific document(s) involved. If the request is being made by an organization other than the manufacturer, justification should be provided on how the standards and designs are being maintained.
Once the CNSC is satisfied that a renewal application is acceptable, it issues a new certificate for the design of the prescribed equipment. The previously issued certificate remains valid until its expiry date, unless the CNSC formally informs the manufacturer and users that the certificate will be decertified. To facilitate tracking, the identification number of the new certificate will be identical to the one for the previously issued certificate except for the revision level and expiry date.
For cost recovery fees, according to the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission Cost Recovery Fees Regulations, a renewal application is considered as the assessment of prescribed equipment identical to a certified prescribed equipment model.
2.4 Certificate duration and notification of expiry
Certificates are issued for a limited duration, usually 15 years for radiation devices and 25 years for Class II prescribed equipment. This is to ensure that prescribed equipment is still supported by the manufacturer and, if still in production, is manufactured to the same standards as were used at the time of the original certification. In the case where the prescribed equipment is no longer supported by the manufacturer, a certificate may be issued, but the duration may be shorter.
In some cases, the manufacturer or other organization wishing to renew a certificate may not have sufficient time to prepare an application. The CNSC may, on a case by case basis, issue a certificate of a shorter duration to allow additional time for the manufacturer or other organization to prepare an application and for CNSC staff to review the information submitted. Such a certificate will generally only be issued once. To obtain such a certificate, the manufacturer or other organization must submit an application requesting a renewal with an explanation of the circumstances. For cost recovery fees, according to the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission Cost Recovery Fees Regulations, such an application is considered as the assessment of prescribed equipment identical to a certified prescribed equipment model.
The CNSC notifies the manufacturer and all users of prescribed equipment three to six months in advance of the impending certificate expiry. If the manufacturer does not plan to renew the certification, it should notify the CNSC. If the manufacturer indicates it will not renew the certificate or there has been no response from the manufacturer, a second notification letter is sent by the CNSC between one and three months prior to the certificate expiry to inform users that the certificate must be renewed and that after the certificate expires they must stop using the prescribed equipment.
2.5 Processing/service standards
In general, the application should be submitted at least one year in advance of when the certificate is required for new designs, six months in advance for amendments (considered similar to a certified model for cost recovery) and three months in advance for renewals with no changes to the design or information on the certificate (considered identical to a certified model for cost recovery).
Applicants should give sufficient advance notice to CNSC staff prior to any design confirmatory tests. Applicants are encouraged to meet with CNSC staff prior to and during the design process to facilitate clear understanding of the regulatory requirements.
3. Completion of the Application Form
This section provides information to assist in completing the various parts of the application form for certification of radiation devices or Class II prescribed equipment. For additional assistance in completing an application, contact a specialist in the Transport Licensing and Strategic Support Division. If you have any questions about how to complete the application form, contact the CNSC through one of the following means:
- telephone: 1-888-229-2672 (toll free in Canada and the United States)
- fax: 613 995-5086
- email: transport@cnsc-ccsn.gc.ca
When preparing an application package, ensure that the information provided on the form and in the attached supporting documents is clear, precise, accurate and complete. If attaching or appending supporting documentation, please specify to which section of the application form the information pertains. Provide the document titles, as well as any cross-references, which should be consistent with the numbered parts of the application. The International System of Units (SI) should be used throughout the application.
3.1 Part A – Applicant's information
A1 Type of request
Indicate if the application is for a new certificate, to amend information on an existing certificate, or to renew an existing certificate. To amend, or renew a certificate, indicate the current certificate number.
A2 Language preference for the certificate
In the appropriate check box, indicate the preferred official Canadian language (English, French or both) for correspondence from the CNSC. A certificate issued in response to this application will be written in the official language(s) selected.
A3 Radiation device or Class II prescribed equipment category
In the appropriate check box, indicate if the application is for a radiation device or Class II prescribed equipment. See the glossary for definitions of terms and phrases used in conjunction with this application form.
A4 Applicant’s organization name
Print or type the name of the person or organization applying for the certificate. Indicate the name as it appears on the proof of legal status documentation, such as the proof of incorporation, the partnership registration, or sole proprietorship.
Name an individual only if that person is a sole proprietor or will be solely responsible for the certification.
A5 Proof of legal status
Applicants must provide proof of their legal status, such as a proof of incorporation, corporation number, or charter, in a separate, appended document, regardless of their country of origin.
If the applicant is a corporation, it needs to submit proof of incorporation and an official corporation profile report that sets out information about the corporation, including:
- legal name
- identification number
- date of incorporation
- registered office address
In Canada, an official corporation profile report can be obtained from Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada for federally incorporated companies under the Canada Business Corporation Act, R.S.S., c. C-44. A business number identifier is assigned to each business or other entity by the Canada Revenue Agency. For provincially incorporated corporations, similar corporation profile reports are available. For more information the provincial department where your corporation was registered may be contacted.
In the United States, corporations, companies and partnerships (business entities) must be registered with the Secretary of State within the state-level government in that state in which the entity is headquartered. Proof of legal status of business entities can be generally obtained by contacting the relevant authorities of the state in which the business entities are headquartered.
Proof of legal status should also be provided when the applicant’s original organization name has changed.
In the space provided, indicate the title of the appended document.
If the applicant is a public institution, specify the name of the enabling legislation (act) under which the institution was created.
A6 Head office address
Provide the legal, physical address of the applicant’s head office, including the complete street name and number (and rural route number if appropriate), city, province or territory, and postal code.
Notify the CNSC as soon as possible of any changes to this information.
Note: A post office box address is not acceptable for a head office address.
A7 Mailing address (if different from above)
Provide the mailing address, if it is different than the head office address, including the complete street name and number, and rural route number if appropriate, city, province or territory, and postal code.
If no address is entered here, a certificate issued in response to the application will be mailed to the head office address. A post office box is acceptable as a mailing address.
Notify the CNSC as soon as possible of any changes to this information.
A8 Manufacturer and distributor
Provide the name and address of the manufacturer if different from the applicant. The name of the manufacturer will appear on the certificate.
Provide the name and address of the distributor if different from the manufacturer and applicant.
Notify the CNSC as soon as possible of any changes to this information.
Note: A change in the name of the manufacturer requires an application for a new certificate.
A9 Canadian representative (for non-Canadian applicants only)
For non-Canadian applicants, provide the name and address of your representative, if one is located in Canada.
Certificates may be issued to a corporation or sole proprietorship located outside Canada. However, applicants should inform the CNSC if they have a representative in Canada.
Notify the CNSC as soon as possible of any changes to this information.
A10 Financial contact person (for applicants subject to cost recovery fees)
Complete this subsection only if you are subject to cost recovery fees for CNSC activities in accordance with the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission Cost Recovery Fees Regulations. Provide the name, title, telephone number and email address of a person in your organization who may be contacted concerning payment matters. Provide the address of the financial office if that address is different from that of the head office.
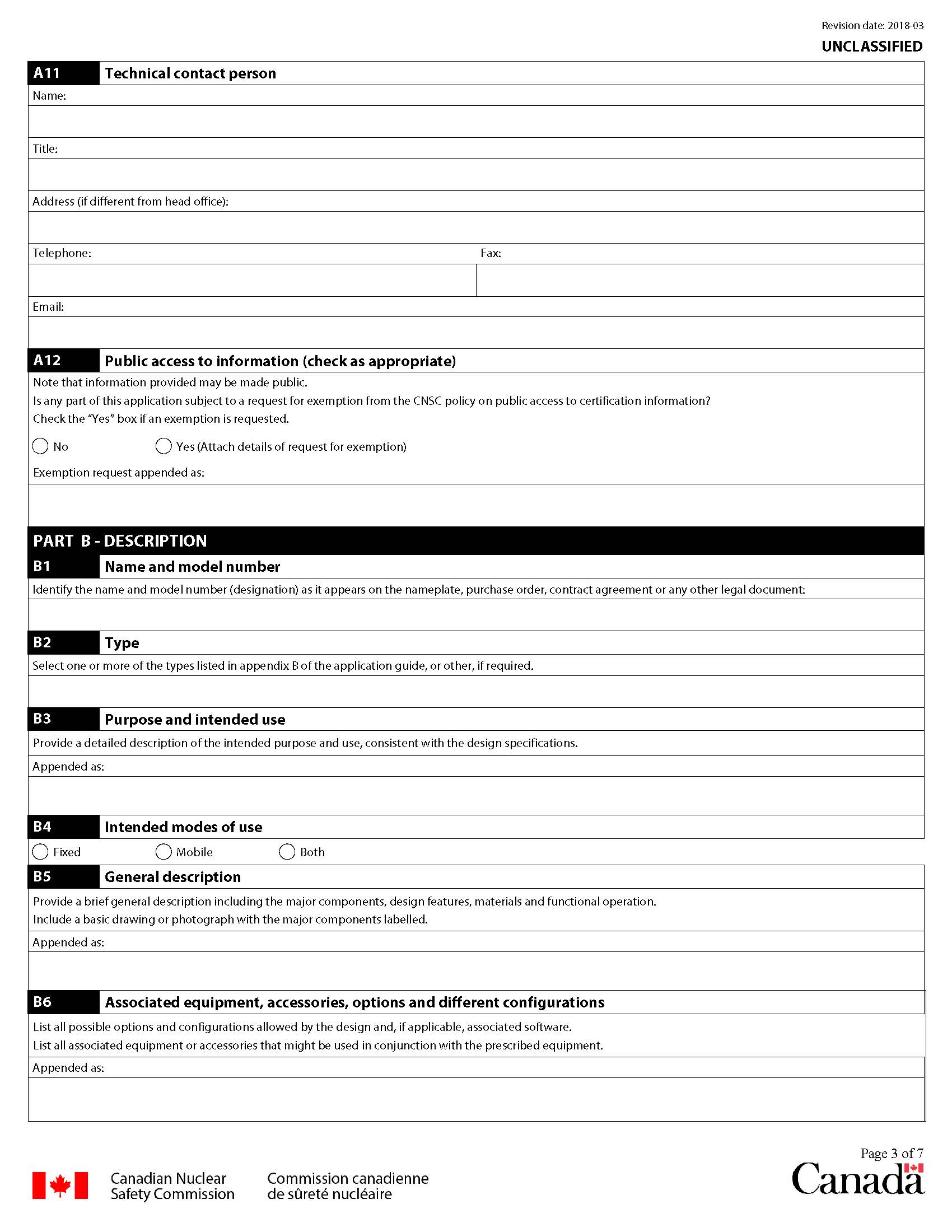
A11 Technical contact person
Provide the name, title, telephone number and email address of a person in your organization who may be contacted concerning technical matters. Provide the address of the technical office if that address is different from that of the head office.
A12 Public access to information
Check the "No" box if information may be made public by the CNSC.
Check the "Yes" box if requesting that the information provided not be disclosed publicly by the CNSC.
Provide the details of the grounds for the request in a separate, appended, document. In the space provided, indicate the title of the appended document.
The CNSC is a government institution subject to the ATIA. As such and pursuant to subsection 4(1) of the ATIA, every person who is a Canadian citizen or a permanent resident has a right to and shall, on request, be given access to any record under the control of a government institution. Exemptions to this right of access are found in sections 13 through 26 of the ATIA. All documents submitted to the CNSC form part of the record as defined in the ATIA and could therefore be subject to disclosure in accordance with the provisions of the ATIA. Section 20 of the ATIA provides an exemption for third-party information.
3.2 Part B – Description
B1 Name and model number
Identify the name and model number of the prescribed equipment, as it appears on the nameplate, purchase order, contract agreement or any other legal document. More than one model number can be identified as long as the designs are similar. All model numbers will be listed on the certificate. If the CNSC considers a model design to be too dissimilar to be covered under the same certificate as other models identified, the applicant will be requested to submit a separate application and pay the associated fees before the model can be certified.
B2 Type
Identify, as closely as possible, the type of prescribed equipment for which certification is being requested. If possible, select one or more of the types listed in appendix A. Note that this list is not exhaustive, and other equipment or device types may be identified.
B3 Purpose and intended use
Provide the intended purpose and use of the prescribed equipment, consistent with the design specifications.
B4 Intended modes of use
In the appropriate check box, indicate if the prescribed equipment is mobile, fixed or both.
B5 General description
Provide a brief general description of the prescribed equipment including the major components, design features, materials and functional operation.
The general description should include a basic drawing or photograph of the prescribed equipment with the major components labelled. Should the application be successful, this description may appear on the certificate.
B6 Associated equipment, accessories, options and different configurations
List all possible options and configurations allowed by the design and, if applicable, associated software.
List all associated equipment or accessories that might be used in conjunction with the prescribed equipment. For an exposure device this could include remote controls, guide tubes, collimators and source changers. For other prescribed equipment this could include targets, filters, integrated imaging devices, or software versions that allow the operation of the equipment in different modes (intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), flattening filter free (FFF), servicing, etc.).
B7 Nuclear substances
Specify all nuclear substances incorporated into the prescribed equipment, using the radionuclide name and mass number, as applicable.
Note: Deuterium, thorium, uranium or an element with an atomic number greater than 92 or a compound or derivate of them, are considered nuclear substances (see definition of nuclear substance in the glossary).
The following information should be specified for each radioactive source used in the prescribed equipment:
- nuclear substance, quantity and activity (list the maximum, where the maximum is the nominal plus manufacturing tolerances)
- physical and chemical form
- name of nuclear source manufacturer
- model number of the source
- the model number of the source holder, if applicable. For exposure devices the source holder should be specified
- indication if the source is certified as special form radioactive material and if so, a copy of the valid Competent Authority certificate for special form radioactive material
- source classification (based on, for example, standards of the American National Standards Institute, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) or similar institutions)
Note: Activity should be expressed in Becquerels (Bq) or multiples thereof (kBq, MBq, etc.).
B8 Accelerator radiation output (for Class II prescribed equipment only)
Specify beam particle types, the maximum energy and current (i.e., cyclotrons, protons, 18 MeV 100 µA), maximum energy, maximum doses for all modes of operation (i.e., linac, photons 15 MV, 600 MU/min, IMRT, FFF), as well as the intensity of radiation to be expected at a reference point for each energy and mode of operation consistent with the design (i.e., 1 metre, at the isocentre) and intended use (append a list of specifications, if necessary). If applicable (neutron generator), specify the intensity and energy of the neutron source term i.e., 25 mSv/h at 1 metre, 2.5 MeV.
3.3 Part C – Design
C1 Technical specifications
The following technical specifications should be provided:
- design specifications for the prescribed equipment, including major associated components and subsystems, and details of the radiation shielding and safety features
- design specifications of radiation sources to be used in the prescribed equipment. If applicable, details should be provided on how the nuclear substance is incorporated into the prescribed equipment
- for particle accelerators, the design specifications for the radiation beam target, specifying the material to be used and the model number(s) for identification
- the overall dimensions and weight of the prescribed equipment, including the weight of any depleted uranium used in the prescribed equipment
- any limitations on the use of the system, such as operating temperature range, vibration levels, pressure, and recommended environmental conditions
- the expected lifetime of use of the prescribed equipment allowed by the design
C2 Technical drawings
Provide details on the design of the prescribed equipment and its components in the form of engineering drawings.
The information listed in section 11 of the Class II Nuclear Facilities and Prescribed Equipment Regulations, or section 12 of the Nuclear Substances and Radiation Devices Regulations must be provided.
Where applicable, include schematic diagrams of radiation safety-related control systems and descriptions of their operation (such as doors and other radiation-enabling machine interlocks, source exposure and beam activation control circuits).
Provide a copy of the overall assembly drawing and indicate the position of any radioactive source or accelerator beam target in respect to the radiation shielding incorporated into the prescribed equipment. A complete set of engineering drawings of the source holder and shielding, with the list of materials, should also be included. These drawings should give sufficient detail to show the construction, dimensions and materials used to enable the reviewer to understand how the various parts of the design are assembled (e.g., welds, bolts, screws, glue) and to understand the operation of any moving parts. Where applicable, detailed drawings of the source capsule and source assembly should be provided.
All drawings should be legible and clearly marked with the release dates, scale, drawing numbers, and an associated parts list or bills of materials. The quantity and type(s) of radiation source(s), and the name and model number of the prescribed equipment must be indicated on the general assembly drawing. A unique number is assigned to each drawing.
When possible, photographs should be provided that show the prescribed equipment from at least two camera angles and include a reference object so that the relative size is evident.
Note: After the certificate has been issued, any significant changes (see glossary for definition) to the prescribed equipment may need to be reassessed and a revised or new certificate may be required. Notify the CNSC immediately about any planned design changes.
C3 Technical and safety standards used
List major technical and safety standards used to design the prescribed equipment, if applicable. Explain how these standards were applied to the design and how compliance to their requirements was verified. If applicable, provide design validation including verification protocols and reports. Attach any relevant test and analysis results.
Some typical organizations that issue standards for prescribed equipment include:
- Canadian Standards Association (CSA)
- Underwriters Laboratories
- Technischer Ãœberwachungs-Verein (Technical Monitoring Association)
- International Electrotechnical Commission
- ISO
- American National Standards Institute
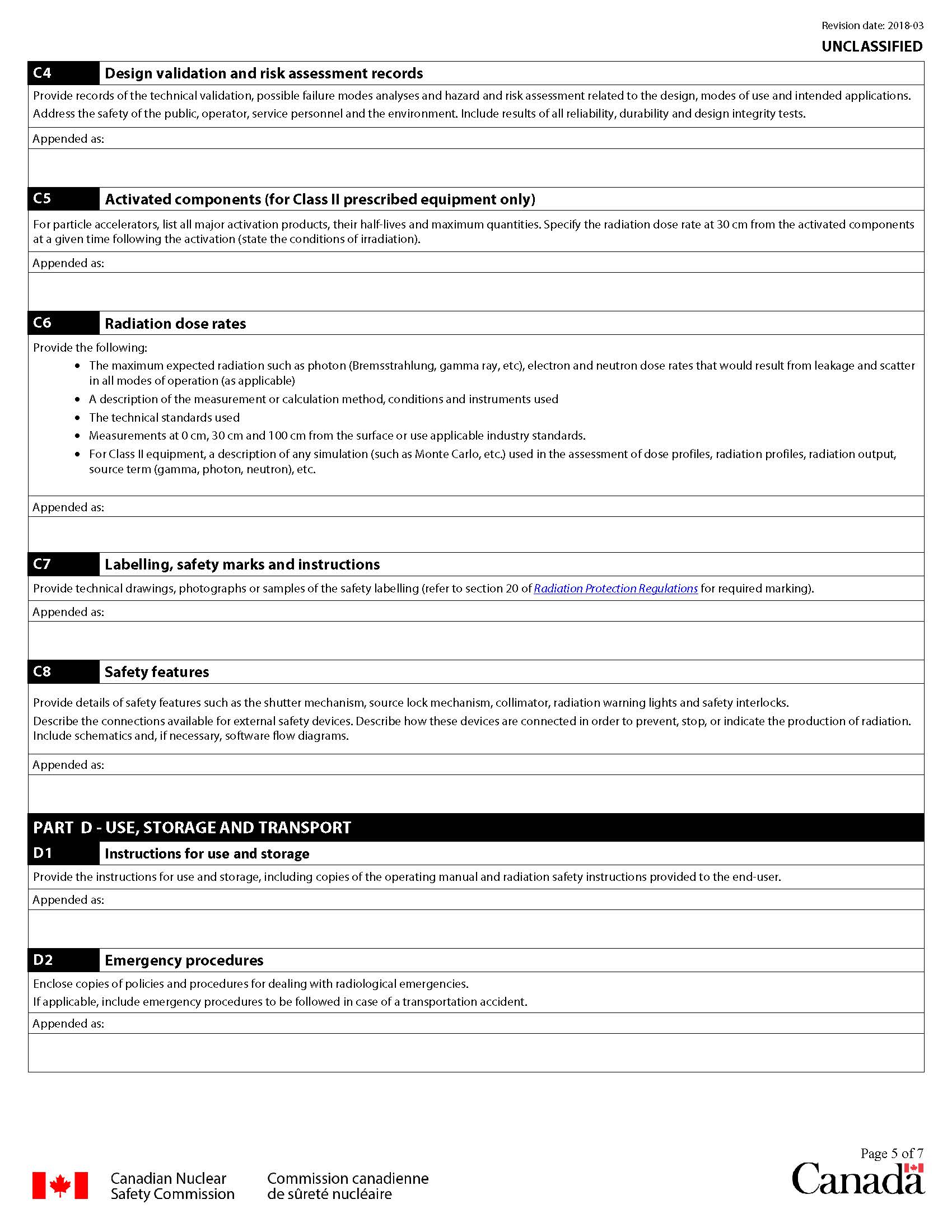
C4 Design validation and risk assessment records
Provide copies of the technical validation records, including test reports. Include records of the failure effect mode analyses, device hazard and risk assessment files. Where appropriate, the application should include:
- details on the prescribed equipment classification, including results of the tests conducted
- results of reliability tests of the shutter mechanism
- details of any other test results pertaining to radiation safety that have been performed
C5 Activated components (for Class II prescribed equipment only)
For particle accelerators:
- list all major activation products that may result from the equipment operations
- list radioisotope names, half-lives, and maximum initial quantities in terms of radioactivity or emitted radiation
- specify the radiation dose rate at 30 cm from the activated components at a given time following the activation (state the conditions of irradiation)
C6 Radiation dose rates
Provide values of the maximum expected radiation such as photon (Bremsstrahlung, gamma ray, etc), electron and neutron dose rates around the equipment in all modes of operation (as applicable) at the maximum activity, including tolerances. Include the measurements and calculation methods used to establish the dose rates. The distances for radiation field measurements should correspond to the values required by technical standards used to specify the survey conditions. Otherwise, use the external surface of the shield, 30 cm and 100 cm from the surface as reference distances. In addition, please provide the following information:
- a description of the radiation profile measurements including details such as the environmental conditions, distances from the source, shutter positions, and exact locations of the radiation detector
- the make and model of the radiation survey meter(s), the date(s) of measurements, and the calibration date(s)
- the maximum dose rate that the prescribed equipment can deliver, the operating conditions that can produce this dose rate, and the areas where this dose rate may exist
- where applicable, indicate the following:
- neutron leakage measurement results
- photon or gamma leakage measurement results
- the neutron source term
- limits to the radiation beam orientation
- locations of activated components and radiation dose rates at 30 cm from those components
Radiation profiles must be submitted for each type of source (nuclear substance) to be used in the prescribed equipment. If the radiation profile may be affected by variation in the design (various series), a radiation profile should be provided for each of the design variations.
Note: If the prescribed equipment incorporates a shutter, measurements must be submitted with the shutter in both the open and the closed position.
If the applicant has used a simulation program based on the Monte Carlo code (i.e., MCNP 5, MCNPX, GEANT, TART, FLUKA, etc.) for the assessment of doses (leakage, activation components, etc.), radiation profiles, radiation output, neutron source term, gamma source term etc., the applicant should provide:
- a brief description of the simulation (geometry, materials, source definition, tallies, doses, graphics)
- input and output files
- shielding techniques employed (variance reduction, geometry splitting, weight windows, Dextran spheres, etc.)
- mesh tally graphics (pdf, psc, jpg, etc.)
- information concerning other related MCNP program used (e.g., ALICE-91), with respective information (as above)
C7 Labelling, safety marks and instructions
Refer to section 20 of the Radiation Protection Regulations for detailed requirements on the marking and labelling of nuclear devices or containers that contain a radioactive nuclear substance, and provide a description of the labelling of the prescribed equipment by including the following information:
- specifications for the equipment nameplate, labels and safety marks, including drawings and photographs as appropriate to show how and where they are affixed to the prescribed equipment
- example of a nameplate and, where applicable, labels, with the information filled in
- safety instructions and warnings for users and service personnel affixed to the prescribed equipment, as applicable
Note that section 20 of the Radiation Protection Regulations requires devices or containers that contain a radioactive nuclear substance to be labelled with:
- the radiation warning symbol set out in Schedule 3 of the regulations and the words "RAYONNEMENT – DANGER – RADIATION"
- the name, quantity, date of measurement and form of the nuclear substance
The applicant should submit the policy and procedure documents for controlling labelling changes associated with equipment upgrades.
C8 Safety features
Provide details of safety features such as the shutter mechanism, source lock mechanism, collimator, radiation warning lights, and safety interlocks.
For prescribed equipment with external safety features, describe the available connections, such as:
- door interlocks
- last person out btns
- emergency stop devices (btns, pull cords, etc.)
- radiation state indicators
- radiation on, off, ready
- beam on, off, radiofrequency, magnet, armed, ready, etc.
- any other safety system that may be in place (i.e. water level switch, movement detector, etc.)
Describe how these devices are connected in order to prevent, stop, or indicate the production of radiation. Include schematics and, if necessary, software flow diagrams.
3.4 Part D – Use, storage and transport
D1 Instructions for use and storage
Provide the instructions pertinent to the use and storage of the prescribed equipment. Include copies of the operating manual and radiation safety instructions provided to the end user. Proposed radiation safety instructions should appropriately reflect the complexities, conditions and hazards involved in using the prescribed equipment.
D2 Emergency procedures
Append or enclose emergency policies and procedures for dealing with accidents in which the prescribed equipment may be involved. Provide a copy of the instructions that are supplied to the end-user. Procedures should include actions to:
- limit the spread of contamination
- reduce the radiation fields
- detect and estimate the quantity of nuclear substances released
- decontaminate the affected site, equipment, workers, and other persons
- monitor radiation releases from the site
- maintain lists of the emergency spill equipment and emergency personnel contacts
Submit the emergency procedures to be followed in case of a transportation accident involving prescribed equipment that is transported frequently (i.e., portable devices such as moisture and density gauges, material analyzers or exposure devices).
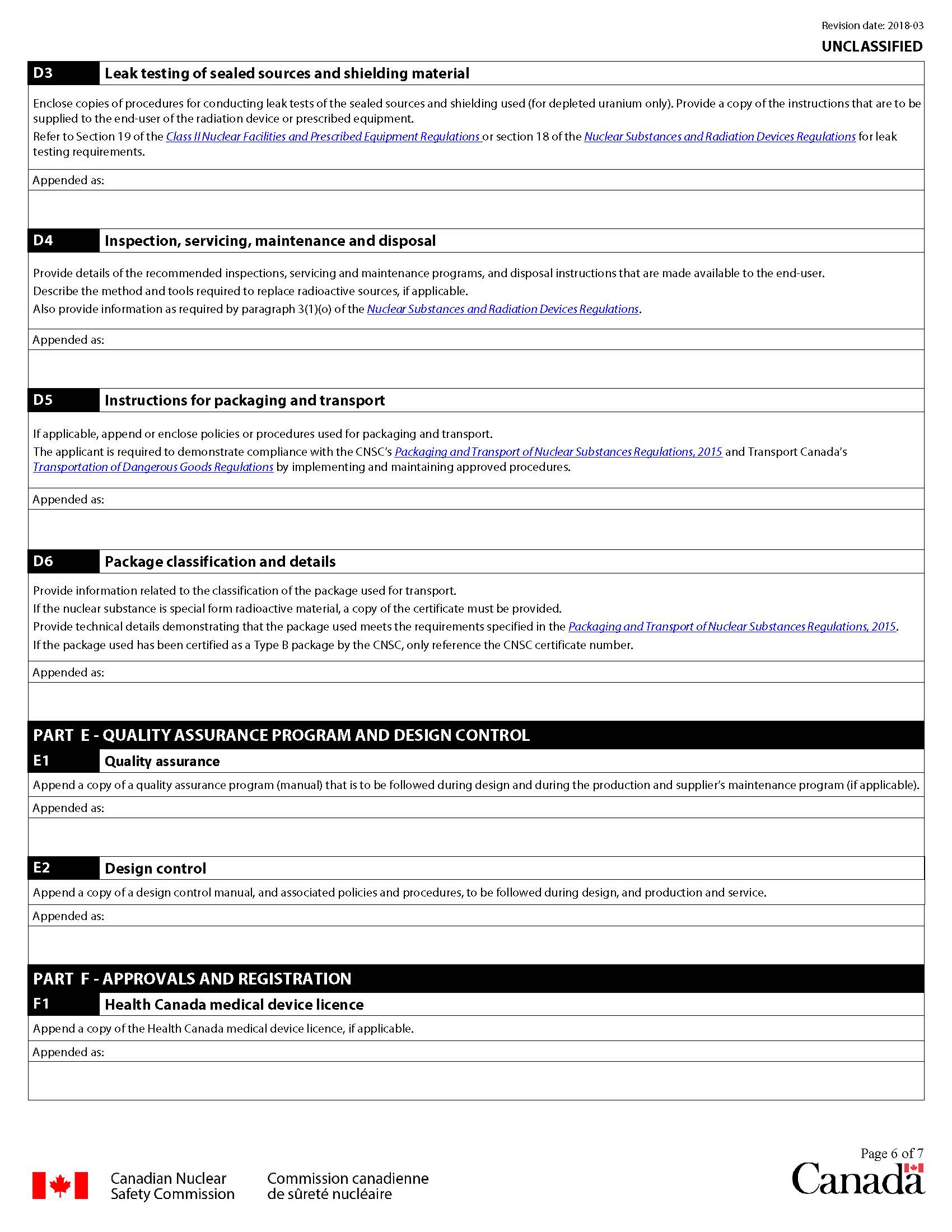
D3 Leak testing of sealed sources and shielding material
Enclose copies of procedures for conducting leak tests of the sealed sources and shielding used (for depleted uranium only) in the prescribed equipment. Provide a copy of the instructions that are provided to the end-user.
All sealed sources greater than 50 MBq must be leak tested using instruments and procedures that enable the detection of a leak of 200 Bq or less of the nuclear substance.
Refer to section 19 of the Class II Nuclear Facilities and Prescribed Equipment Regulations or section 18 of the Nuclear Substances and Radiation Devices Regulations for leak testing requirements.
D4 Inspection, servicing, maintenance and disposal
Provide details of the recommended inspection, servicing program, maintenance program, and describe the conditions of retiring the prescribed equipment from operation and disposal of the radiation source(s) or activated components supplied to the end-user. Also provide information as required by paragraph 3(1)(o) of the Nuclear Substances and Radiation Devices Regulations.
Provide a list of the parts that require maintenance and servicing:
- by the end user
- by an authorized service provider
Also indicate the parts for which maintenance or service is not required.
Provide the procedure for source replacement, if applicable, and indicate if this can only be performed by the manufacturer.
D5 Instructions for packaging and transport
The applicant is required to demonstrate compliance with the CNSC’s Packaging and Transport of Nuclear Substances Regulations, 2015 and Transport Canada’s Transportation of Dangerous Goods Regulations, by implementing and maintaining approved procedures.
The following should be submitted with the application:
- instructions for packing, unpacking and transporting the radioactive material. These should include:
- a copy of the packaging instructions to be supplied to the end-user for the return of the radioactive material
- a copy of the preparation for shipping instructions supplied to the end-user
- all actions required to properly prepare the radioactive material for transport, including items such as properly closing or locking shutters, or additional packaging, as applicable
- a copy of maintenance procedures for the package, if the package is to be re-used
If the radioactive material is transported separately from the prescribed equipment, only information on the transport of the radioactive material is required.
D6 Package classification and details
Specify the classification of the package, as follows:
- excepted packages (instrument or article, limited quantity of material, articles manufactured from natural uranium or depleted uranium or natural thorium)
- Type A packages
- Type B packages
If a claim is made that the radioactive source is special form radioactive material, a copy of the valid Competent Authority certificate must be submitted.
For a radiation device to be classified as an instrument or article, the source and its shielding must be part of the device and enclosed by the body of the device. Source holders alone are not instruments.
If the package used for the transport of the prescribed equipment has been certified as a Type B package by the CNSC, only the reference to the CNSC certificate number is required.
For other packages, the following information must be submitted for assessment of the proposed package:
- details of the technical specifications of the package design, including specifications of the package materials, design and construction. Specify if additional packaging is required to meet the package classification
- information that demonstrates that the package meets the requirements specified in the Packaging and Transport of Nuclear Substances Regulations, 2015 if applicable. This information includes details on the test results demonstrating the package can withstand normal conditions of transport
- details of the means to provide fastening and sealing of the shutter(s) or source(s), prior to transportation. This information is not required if the source is shipped separate from the prescribed equipment package
- details of any additional markings that will be affixed to the package
The provision of the above information will allow the CNSC to assess whether an acceptable package is available for transport of the prescribed equipment at the time of certification. This does not preclude using a package other than that specified above at a later date, provided that the requirements of the Packaging and Transport of Nuclear Substances Regulations, 2015 are followed.
A separate application, as per the Packaging and Transport of Nuclear Substances Regulations, 2015 must be submitted to the CNSC for the certification of a package or for the endorsement of a foreign certification as a Type B package. When a package has been certified as a Type B package, the user must register its use separately and may only transport the package after receiving confirmation of the registration.
A radiation device used as a Type B package must be certified by the CNSC both as a radiation device and as a Type B package.
3.5 Part E – Quality assurance program and design control
E1 Quality assurance
A quality assurance (QA) program is required for the design and manufacture of prescribed equipment. List documents used in the QA program. A copy of the QA manual should be provided to the CNSC for review. In addition, if the applicant is ISO registered or certified, provide a copy of the registration or certification obtained and the approval date.
Append or enclose the policy regarding the QA program that was followed during the design of the prescribed equipment and that will be followed during its production and service.
E2 Design control
Provide copies of the design control manual and associated policies to be followed during the design of the prescribed equipment, as well as during production.
3.6 Part F – Approvals and registrations
F1 Health Canada medical device licence
Medical devices are regulated by Health Canada pursuant to the Food and Drugs Act and through the Medical Devices Regulations. The regulatory requirements apply to the manufacturing, sale, advertising for sale and importation of medical devices. Manufacturers must ensure that their medical devices meet the safety and effectiveness requirements as defined in the Medical Devices Regulations and are approved for the Canadian market.
Medical devices require a licence issued by Health Canada prior to certification by the CNSC. A copy of the Health Canada licence should be included with the application.
F2 Medical device approvals and registrations
Include a copy of the following documents, if applicable:
- United States Food and Drug Administration medical device registration
- European Union Council medical device directive registration
- CSA approval
F3 Other applicable jurisdiction approvals and registrations
Include a copy of the following documents, if applicable:
- ISO series (and related standards) registration
- certificate(s) of compliance with applicable technical standards
- United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission registration
- approvals of pertinent national, provincial or state authorities
3.7 Part G – Legal signing authority
To comply with section 15 of the General Nuclear Safety and Control Regulations, every applicant must provide information to the CNSC about its legal representatives.
G1 Applicant authority
This person has the authority to apply on behalf of the applicant, and by doing so, certifies that the information submitted is true and correct to the best of their knowledge.
This person acts for the applicant in dealings with the CNSC. Provide the name, telephone number, fax number and email address of the person.
4. Cost Recovery Fees Regulations
As set out in the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission Cost Recovery Fees Regulations, the CNSC charges fees for its regulatory activities. Cost recovery fees and exemptions are listed in these regulations.
Some licensees are exempt from paying fees, including the following:
- educational institutions
- not-for-profit health care institutions that receive funds from federal, provincial, or municipal governments
- government departments listed in Schedules I and II of the Financial Administration Act
- provincial and local governments
For details on exemptions, refer to the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission Cost Recovery Fees Regulations.
Applicants who are subject to cost recovery fees must pay the fees that are assessed according to the extent of the certification activity. The fee schedule is posted on the CNSC website. For assistance in determining the fees particular to a specific prescribed equipment, applicants should contact the CNSC cost recovery unit listed below.
Payment of cost recovery fees must accompany the certification application. Payment may be made by cheque or money order made payable to the Receiver General for Canada, or by credit card. To arrange payment by credit card, applicants should contact the Cost Recovery Officer in the CNSC Accounting, Systems and Controls Division in Ottawa at:
- Telephone: 613-991-9791 or 1-888-229-2672 (toll free in Canada and the United States)
- Fax: 613-995-5086
- Email: finance@cnsc-ccsn.gc.ca
Appendix A: Application Form for Certification of Radiation Devices or Class II Prescribed Equipment




Appendix B: Radiation Devices and Class II Prescribed Equipment
- Radiation devices
- Attenuation correction device
- Beta backscatter gauge
- Bone mineral analyzer
- Brachytherapy seed loaderCalibrator
- Control unit – Exposure device crawler
- Core discharge monitor
- Dewpointer
- Electron capture detector
- Exposure device
- Exposure device – cable
- Exposure device – crawler
- Exposure device – mobile
- Exposure device – pneumatic
- Fixed gauge
- Intravascular brachytherapy
- Ion chamber detector
- Irradiator
- Liquid scintillation counter
- Logging
- Low-energy imaging
- Material analyzer
- Medical calibrator
- Medical irradiator
- Monitor
- Portable gauge
- Profile attenuation correction system
- Radioluminescent device
- Smoke detector
- Static detector
- Static eliminator
- Surge voltage protector
- X-ray fluorescence analyzer
- Other (specify)
- Class II prescribed equipment
- Brachytherapy machine
- Calibrator &ndah; Class II
- Cyclotron
- Geophysical logging accelerator
- High dose rate afterloader
- Irradiator – Class II
- Low dose rate afterloader
- Linear accelerator
- Medical accelerator
- Mobile accelerator
- Neutron generator
- Radioisotope neutron source
- Research accelerator
- Self-shielded accelerator
- Teletherapy irradiator
- Teletherapy machine
- Other – Class II (specify)
Glossary
- certification
- A written attestation from the Commission, or from a designated officer authorized by it, that a person is qualified to carry out licensed activities (including the duties of a given position).
- certified
- Certified by the Commission under paragraph 21(1)(h) or (i) of the Nuclear Safety and Control Act or by a designated officer authorized under paragraph 37(2)(a) or (b) of the Act.
- Class II prescribed equipment certificate
- A document issued by the Commission or by a designated officer authorized under paragraph 37(2)(a) of the Nuclear Safety and Control Act, indicating that a model of Class II prescribed equipment is certified, or authorized under paragraph 37(2)(b) of the Act, indicating that a person is certified.
- Class II prescribed equipment
- Means:
- an irradiator that uses more than 1015 Bq of a nuclear substance
- an irradiator that requires shielding which is not part of the irradiator and that is designed to deliver a dose of radiation at a rate exceeding 1 centigray per minute at a distance of 1 m
- a radioactive source teletherapy machine
- a particle accelerator that is capable of producing nuclear energy and has a beam energy of less than 50 MeV (mega electron volts) for beams of particles with a mass equal to or less than 4 atomic mass units
- a particle accelerator that is capable of producing nuclear energy and has a beam energy of no more than 15 MeV per atomic mass unit for beams of particles with a mass greater than 4 atomic mass units
- a brachytherapy remote afterloader
- exposure device
- A radiation device that is designed for carrying out gamma radiography, and includes any accessory to the device such as a sealed source assembly, a drive mechanism, a sealed source assembly guide tube and an exposure head.
- irradiator
- A device that is designed to contain a nuclear substance and to deliver controlled doses of radiation from that substance to any target, except persons.
- maintenance
- The organized activities, both administrative and technical, to keep Class II prescribed equipment and radiation devices, as well as structures, systems and components, in good operating condition. Note: For reactor facilities, maintenance includes repair aspects.
- nuclear substance
- One of the following:
- deuterium, thorium, uranium or an element with an atomic number greater than 92
- a derivative or compound of deuterium, thorium, uranium or of an element with an atomic number greater than 92
- a radioactive nuclide
- a substance that is prescribed as being capable of releasing nuclear energy or as being required for the production or use of nuclear energy
- a radioactive by-product of the development, production or use of nuclear energy
- a radioactive substance or radioactive thing that was used for the development or production, or in connection with the use, of nuclear energy
- operate
- For an exposure device, operate includes coupling the drive mechanism to the exposure device, uncoupling the drive mechanism from the exposure device, locking or unlocking the exposure device, and all activities involving the device that take place while the sealed source assembly is not locked inside the device in the fully shielded position.
For other devices, equipment or facilities, operate means turning on and using the device, equipment or facility for its intended purpose and in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. Operate includes minor upkeep as per the operating manual.
- particle accelerator
- A device that accelerates electrically charged particles to extremely high speeds, for the purpose of inducing high energy reactions or producing high energy radiation.
- radioactive source teletherapy machine
- A teletherapy machine that is designed to deliver doses of radiation produced by a nuclear substance.
- radiation device
- Either of the following:
- a device that contains more than the exemption quantity of a nuclear substance and that enables the nuclear substance to be used for its radiation properties
- a device that contains a radium luminous compound
- radiation device certificate
- A document issued by the Commission or by a designated officer, authorized under paragraph 37(2)(a) or (b) of the Nuclear Safety and Control Act, indicating that prescribed equipment or a person is certified.
- sealed source
- A radioactive nuclear substance in a sealed capsule or in a cover to which the substance is bonded, where the capsule or cover is strong enough to prevent contact with or the dispersion of the substance under the conditions for which the capsule or cover is designed.
- sealed source assembly
- A sealed source designed to be used in an exposure device, which includes the components that are permanently attached to the sealed source.
- special form radioactive material
- An indispersible solid radioactive material or a sealed capsule containing radioactive material and that has demonstrated that it has met the requirements for special form radioactive material, as specified in the International Atomic Energy Agency Regulations, and for which a certificate of approval from a competent authority has been issued.
- service
- Any maintenance of prescribed equipment, including installation, repair or dismantling, other than maintenance that:
- constitutes routine operating procedures as indicated in the manufacturer’s operating manual for the device; or
- is authorized in the licence issued in respect of the possession or use of the device
Sealed source installation or replacement, as well as any repair that could expose the sealed source, reduce the shielding around the sealed source, or affect the drive control for radiotherapy, is considered as servicing.
- significant change
- A change in the equipment’s characteristics, principles of operation and specifications that could reasonably be expected to affect the safety or effectiveness of the equipment or the safety of the facility in which it is operated, such as:
- a change in the intended use of the device, including any new or extended use (teletherapy machine used as an irradiator)
- a change or upgrade of software that allows the machine to work in a different mode or energy level outside of the original certification (IMRT, FFF, higher dose rates, etc.)
- retrofit for a new head or collimator that would allow a different mode or operation producing higher leakage rates
- increase of activity of the sources
- a change in the model name or machine configuration such that it does not correspond with the certificate or significant changes to device labelling – it is important for the machine to be identifiable in the field
CNSC Regulatory Document Series
Facilities and activities within the nuclear sector in Canada are regulated by the Canadian Nuclear Safety Commission (CNSC). In addition to the Nuclear Safety and Control Act and associated regulations, these facilities and activities may also be required to comply with other regulatory instruments such as regulatory documents or standards.
Effective April 2013, the CNSC's catalogue of existing and planned regulatory documents has been organized under three key categories and twenty-five series, as set out below. Regulatory documents produced by the CNSC fall under one of the following series:
- 1.0 Regulated facilities and activities
- Series 1.1 Reactor facilities
- 1.2 Class IB facilities
- 1.3 Uranium mines and mills
- 1.4 Class II facilities
- 1.5 Certification of prescribed equipment
- 1.6 Nuclear substances and radiation devices
- 2.0 Safety and control areas
- Series 2.1 Management system
- 2.2 Human performance management
- 2.3 Operating performance
- 2.4 Safety analysis
- 2.5 Physical design
- 2.6 Fitness for service
- 2.7 Radiation protection
- 2.8 Conventional health and safety
- 2.9 Environmental protection
- 2.10 Emergency management and fire protection
- 2.11 Waste management
- 2.12 Security
- 2.13 Safeguards and non-proliferation
- 2.14 Packaging and transport
- 3.0 Other regulatory areas
- Series 3.1 Reporting requirements
- 3.2 Public and Aboriginal engagement
- 3.3 Financial guarantees
- 3.4 Commission proceedings
- 3.5 CNSC processes and practices
- 3.6 Glossary of CNSC terminology
Note: The regulatory document series may be adjusted periodically by the CNSC. Each regulatory document series listed above may contain multiple regulatory documents. For the latest list of regulatory documents, visit the CNSC's website.